- Emergency Ambulance Services
- 8606811111
- 0471-4077777, 0471-7177888
- gro@sutpattom.com
Vascular Day – August 06 Life, Lifestyle And Lifestyle Disease
Dr. M. Unnikrishnan, Senoir Vascular Surgeon, SUT Hospital, Pattom
Dr. B. C. Roy National Award 2016, President, Vascular Society of India
Of diverse causes leading to ill health in us, non-communicable and communicable diseases, cancer and accidents are the front runners. Non-communicable diseases also known as “Lifestyle diseases” are on the increase in view of demographic transition, with resultant longer life expectancy in our population. Risk factors for lifestyle diseases are age above 60yrs and male gender, forming NONMODIFIABLEfactors while Smoking, Diabetes, Obesity, High cholesterol levels, Hypertension and Physical inactivity in that order form the MODIFIABLE determinants of lifestyle diseases.
All systems in our body are meticulously and incredibly crafted by GOD.The three components of circulatory system consisting of HEART-THE PUMP, blood- as carrier of oxygen/carbon-di-oxide, metabolites, glucose and hormonesetc. through a very extensive chain of blood vessels – Arteries (vessels carrying pure blood) and Veins (vessels carrying impure blood). Vascular& Endovascular surgery pertains to diagnosis, treatment strategies, preventive measures, research activities and teaching regarding diseases of blood vessels. Afflictions of arteries and veins form pre-dominant subset since they form more than 95% of vascular diseases. AORTA (MAHADHAMANI)- the PRINCIPAL largest blood vessel carrying pure bloodand arterial branches thereof are involved with the disease process called Atherosclerosis. Aorta is commonly afflicted with ballooning of its walls called “ANEURYSM” and Arteries narrowing its interior due to cholesterol and fat materials. The former upon enlarging to a critical size leads to a break in its wall which could be fatal, If not addressed expeditiously. On the other hand narrowing of arteries leads to decreased pure blood supply to the appropriate organs in varying levels leading to inadequate functional capacity. In contrast, veins (impure blood vessels) are involved with VARICOSE VEINS in the legs and clotting of blood in the leg veins with a possibility of traversing upwards to Heart and Lungs known as VENOUS THROMBO EMBOLIC disease.
By and large arterial/aortic diseases are more serious and limb/organ/life threatening potential, and thus there is a saying that “Functional age of the patient is related to status of his/her arteries”.
COMMON ARTERIAL/AORTIC DISEASES
- A. ARTERIAL INSUFFIENCY TO LEGS
- Sudden blockade of arteries
- Peripheral Artery Disease
When artery of the leg(s) gets suddenly blocked from blood clot / material from heart/ aorta, the patient develops abrupt and severe pain and would not be able to walk as he did before. This condition, called ARTERIAL EMBOLISM mandatesanopen surgery to remove the offending clot and reinstate limb perfusion. The Golden period of ischemia (duration of arterial blockade) is generally 6-8 hours.So,clot removal has to be done at the earliest to avoid damage to tissues. However, When the patient presents at/more than 48hrs, clot lysis by medicines may be of some help. Anti-coagulation medication needs to be continued to treat the original cardiac problem. In an elderly patient, blood clotting at the site of cholesterol deposition also needs to be considered in acute presentations.
When atherosclerosis leads to cholesterol/fat deposition inside the arteries of the legs gradually decreasing blood supply to legs, Patientinitially feels cramps in his calf/thigh muscles on walking. As time goes on, the blockade may become complete, leading to severe pain in legs upon walking a small distance. If not attended to at this stage, patient may develop pain in legs even while resting, maydevelop spontaneous ulcers(without injury) refusing to heal and develop blackish toes/foot. If urgent medical attention is not provided, there is a high risk of losing one’s own limb with its attendant difficulties.
History, physical examination and duplex evaluation would provide the status of limb circulation and if serious, CT Angiogram needs to be done to image extent and nature of arterial blockade. Initial treatment is medical management and for more serious situations key-hole surgery (Balloon Angioplasty / stenting) is necessary. When the latter is not possible or fails, Bypass procedure using superficial vein in the leg or artificial graft becomes necessary.
Attention to Risk factor modifications and graded exercise (pain free walking distance) are advised in the early stages. Key-hole surgery is appropriate for significant disability to improve quality of life and increase walking distance. Open surgery is reserved for critical limb ischemia to save the limb.
It is true to say “STATUS OF LEG(S) MAY DECIDE LIFE STATUS”.

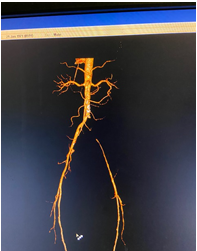
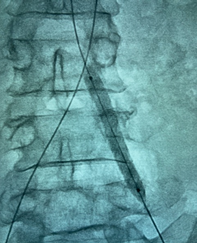
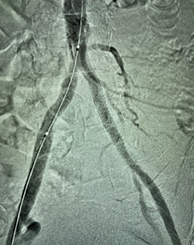
(Artery to left leg blocked at its origin from aorta)
(Key-hole endovascular balloon dilatation in progress)
(The opened up & stented leg artery) - B. CAROTID ARTERY DISEASE/STROKE
- C. ABDOMINAL AORTIC ANEURYSM
Stroke otherwise known as paralysis of one side of the body with/without difficulty in speaking is caused by abrupt cessation of arterial blood to parts of brain or bleeding inside the brain. Of the many causes leading tostroke, cholesterol/fat deposition in brain artery (Atheromatous plaque in internal carotid artery) forms the principal cause. A patient having a plaque in carotid artery may develop transient weakness of his limbs or loss of speech lasting minutes/hours forming a pilot event. In this context, patient has to be evaluated with duplex scan and thereafter CT Angiogram to prove presence of an offending plaque. Medical management is instituted immediately and within 3-4 weeks of the event, definitive treatment in the form of CAROTID ENDARTERECTOMY (removal of the plaque) or CAROTID ARTERY STENTINGis scheduled.
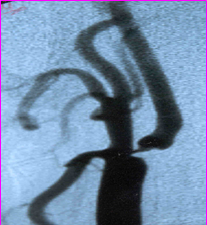
(The above figure shows severe narrowing of brain artery with pre-stroke {red arrow})
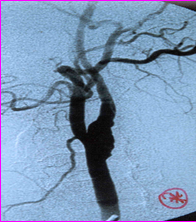
(Post-op angiogram picture showing normalized brain artery {red arrow})
WhenAORTA (MAHADHAMANI) in our abdomen is of 2cm or less in diameter, in a small subset (less than 5%) of subjects above 60yrs may undergo dilatation/ ballooning which is called an ANEURYSM. As time goes on, dilatation keeps on increasing in size and is prone to rupture if not treated electively. Although the threshold for intervention is considered 5.5cms of size, smoking, lung disease and hypertension are known to expediate higher incidence of rupture. Clinical examination followed by ultrasound evaluation of abdomen suggests the aneurysm. CT Aortogram confirms the aneurysm, its size,extent and need for timing of intervention. Open conventional surgery is the first choice for treatment and endovascular aneurysm repair is considered when patients general/cardiac condition is not favorable. While open surgery is durable, the endovascular surgery requires burdensome surveillance and occasionally secondary procedures.
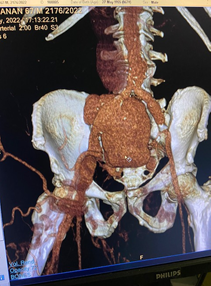
(CT angiogram showing iliac artery aneurysm10cm in size)
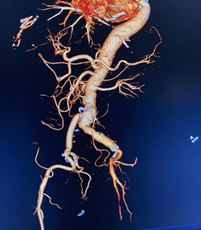
(Post op CT Angiogram showing patent vascular graft)
LESS COMMON ARTERIAL/AORTIC DISEASES
- A. ATHEROSCLEROTICTHORACIC/AORTIC ARCH ANEURYSM
- B. AORTIC DISSECTION
Atherosclerotic aneurysms are less common in thoracic and aortic arch domains. When the aneurysm grows to a size of 6cm, treatment is necessary. These aneurysms can produce pressure symptoms and often rupture resulting in hemothorax necessitating immediate attention.
By and large Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm is detected incidentally, but Aortic Arch Aneurysm may present with chest discomfort and or hoarseness of voice due to left recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy. CT Aortogram is the imaging technique of choice defining the size, extentand presence of clots if any. Open surgery is effective for treatment when a large diameter prosthetic graft is used to repair the aneurysm with the help of circulatory support. However, with the advent of STENT GRAFT (prosthetic graft supported with multiple Ni-Tinol rings) is introduced through a key-hole (endovascular) procedure from the groin artery.
Aortic Arch Aneurysms were treated by open technique using cardio-pulmonary bypass with varying duration of circulatory arrest/ Anti-grade cerebral perfusion. However, the current choice is HYBRID AORTIC ARCH aneurysm repair using best of both open and endovascular strategies.
Aortic Dissection denotes a tear in the inner wall of aorta through which blood sweeps into the aortic wall resulting in an intra-mural haematoma. The tear can occur at the root of aorta (Stanford A) or after the origin of left subclavian artery at the beginning of descending thoracic aorta (Stanford B). This disease process results due go a congenital weaking of aortic wall complicated by high systemic hypertension. While Stanford A dissection needs immediate surgery to save life, Stanford B dissection could be managed by medications in the setting of ICU unless complicated by mal-perfusion of major arterial branches. Blood pressure control is the key to medical treatment and three months after the incident, endovascular stent graft procedure needs to be done to save life and remodel the aorta.
SUMMARY
Lifestyle diseases are principally the result of non-modifiable risk factors of growing old (> 60yrs) and male gender interplaying with modifiable risk factors of smoking, diabetes, obesity, hyperlipidemia,hypertension and physical inactivity. Diet control and moderate exercise help in optimizing modifiable risk factor particularly stopping use of tobacco and alcohol abuse. Walking a kilometer or on treadmill for 15minutes/ 5days a week are practical virtues to keep physical fitness. Vascular diseases still may occur but it’s fury may be attenuated by optimal control of risk factors in male subjects over 60yrs.
Initial assessment and appropriate medications would benefit when vascular afflictions occur with mild to moderate disability. When symptoms override to reduce quality of life, key-hole surgery (minimally invasive endovascular procedures- Balloon angioplasty/stenting) may be adopted to. Serious symptoms with confirmation of organ dysfunction mandates either endovascular or open conventional surgery to save limb/organ/life along with supported by appropriate medications.
VASCULAR CAPSULES
- “MITHAMAYI AAHARAM, MITHAMAYITENKILUM VYAYAMAM”
- “WALK A MILE TO LIVE WITH A SMILE”
- “STATUS OF LEGS MAY DECIDE LIFE STATUS”