- Emergency Ambulance Services
- 8606811111
- 0471-4077777, 0471-7177888
- gro@sutpattom.com
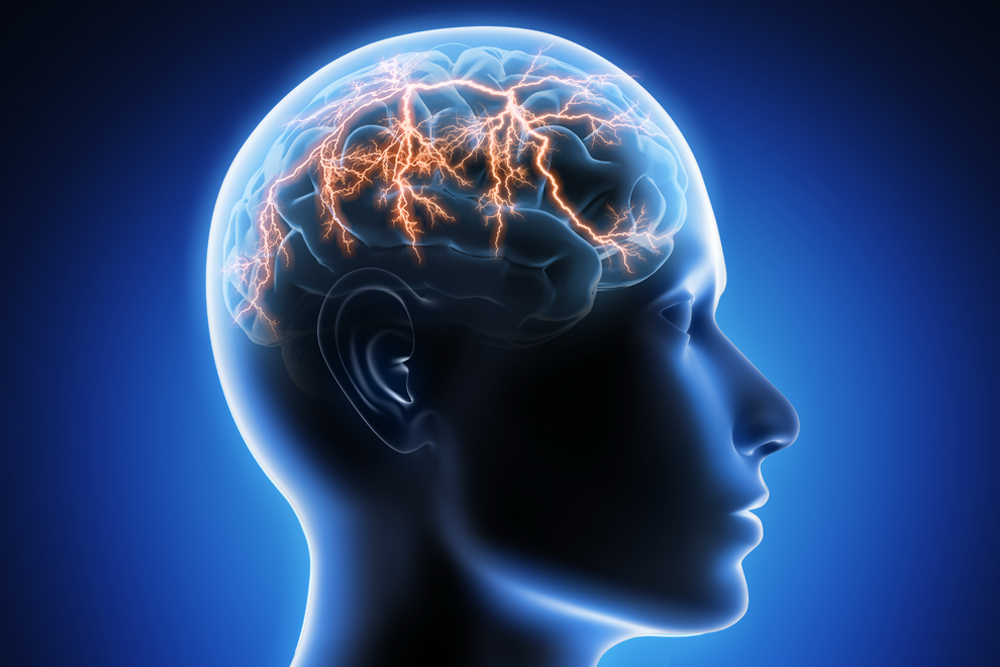
A Brief about Brain Trauma
A head injury is any sort of injury to one’s brain, skull, or scalp. Some of the common head injuries include concussions, skull fractures, and scalp wounds. The effect and treatment for head injury is often considered after knowing the cause of head injury and how deep the injury.
Head injuries can be broadly classified as closed or open. A closed head injury is any injury that doesn’t break the skull. An open head injury breaks the skull and enters the brain. Head injuries caused by a blow to the head are usually associated with:
- Road accidents
- Slip and falls
- Physical assaults
- Sports-related accidents
In most cases, your skull will protect one’s brain from serious harm. However, injuries severe enough to cause head injury can also be associated with injuries to the spine.
Proper diagnosis is important for head injury. Some minor head injuries bleed a lot, while some major injuries don’t bleed at all. It’s important to treat all head injuries seriously and get them assessed by a doctor. Head injury is the leading cause of accidental death and disability in developing countries. Traumatic brain injury can cause permanent neurological deficit and long term sequela severely affecting the quality of life. Head trauma can range from a minor concussion- which is a transient loss of consciousness to severe brain bleeding leading to coma or death.
The brain is a soft organ made of neural structures. The brain controls every act and emotion of everyone’s life. Depending on the force and severity of the trauma, a head injury could be a fracture, brain tissue damage or tearing of blood vessels. The injuries may occur at the site or diagonally opposite to the site of impact.
The bleeding could be outside or inside the brain covering. Small hematomas (localised bleeding of blood vessels) are usually not life-threatening but can cause seizures, headaches, and vomiting. Severe head injury causes decreased levels of consciousness, weakness of limbs and cranial nerve dysfunction.
A hematoma is a collection, or clotting, of blood outside the blood vessels. It can be very serious if a hematoma occurs in the brain. The clotting can lead to pressure building up inside your skull. This can cause you to lose consciousness or result in permanent brain damage. When the hematomas expand in size they can cause an increase in brain pressure, brain herniation and rapid deterioration of sensorium of the patient leading to breathing and circulatory disturbances. Emergency surgery is needed to evacuate the bleeding and reduce brain pressure, a delay can lead to permanent brain damage. At times, the fractured skull may compress the underlying brain which can cause seizures or infections. Such patients also need surgery to remove the fractured bone which is pressing onto the brain.
A concussion occurs when the blow to the head is severe. It’s thought to be the result of the brain hitting against the hard walls of your skull or the forces of sudden acceleration and deceleration. The effects are considered temporary, but a concern when repeated concussion occurs.
Any trauma victim with symptoms of loss of consciousness, headache, vomiting, seizure, bleeding from nose, a loss of consciousness, serious disorientation, an inability to focus the eyes, memory loss, leaking of clear fluid from the ear or the nose, mouth or ear and scalp wound with swelling requires clinical examination and assessment to rule out brain injury and skull fracture. A CT scan is mandatory to investigate an aberration. MRI scanning may be needed in cases where the CT is inconclusive and a diffuse axonal brain injury is suspected. Any patient suspected to have a head injury should be immediately shifted to the nearest hospital with a CT scanning facility and assessed by a neurosurgeon.
The head injury should be detected as early as possible. Head injury that causes bleeding requires surgery, the best results are obtained when the surgery is done at the earliest.
After head trauma, patients are usually put on anticonvulsant drugs to avoid seizures which may have to be continued for up to a year depending on the severity of the injury. Minor bleeds usually resolve in six weeks and patients can return to a normal routine. Rehabilitation is necessary for patients with serious brain trauma, this involves physiotherapy, speech therapy, and supportive care.
Avoiding rash and drunken driving will go a long way in reducing the incidence of accidents and thereby head trauma.
Wearing helmets, driving at moderate speed, wearing seat belts, abstaining from the use of cell phones while on the wheel and abiding by traffic rules are simple preventive steps each of us can follow. Better roads with proper traffic signs and strict enforcement of laws are measures required from authorities.
SUT Pattom, one of the leading hospitals in Kerala handles head injury cases with utmost care and dedication. The treatment is a mixture of well known practices of modern medicine assisted with innovative technology. SUT Pattom has the best fleet of doctors and surgeons to take care of every patient with a promise of life and hope.