- Emergency Ambulance Services
- 8606811111
- 0471-4077777, 0471-7177888
- gro@sutpattom.com
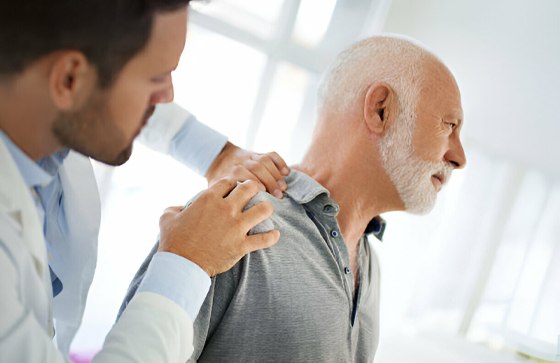
Recurrent Shoulder Dislocation: Causes, Evaluation, and Treatment
Shoulder dislocation, a common orthopaedic injury, can be a painful and debilitating condition. Recurrent shoulder dislocation, where the shoulder repeatedly pops out of its socket, poses unique challenges and requires careful evaluation and treatment.
Shoulder dislocation occurs when the upper arm bone (humerus) comes out of the shoulder socket (glenoid). Recurrent dislocations often occur due to ligament laxity or structural abnormalities that make the shoulder more prone to instability. The primary causes of recurrent shoulder dislocation include Traumatic dislocation, Muscle weakness or Imbalance, Labral tears and Congenital factors.
When evaluating recurrent shoulder dislocations, healthcare providers typically follow a systematic approach that may include:
Medical History: Understanding the patient’s history of shoulder dislocations, previous treatments, and any underlying conditions is crucial.
Physical Examination: A thorough physical exam helps assess shoulder stability, range of motion, muscle strength, and any signs of structural abnormalities.
Imaging Studies: X-rays, MRI scans, or CT scans may be prescribed to visualize the shoulder joint, identify structural issues like labral tears or bone abnormalities, and assess the extent of damage.
Functional Assessment: Assessing how the shoulder functions in daily activities and sports-specific movements can provide valuable insights into the severity of instability.
Treatment Options
The treatment approach for recurrent shoulder dislocation depends on various factors, including the underlying cause, severity of instability, and the patient’s lifestyle and activity level. Common treatment options include Conservative Management, Medications, Surgical Intervention, Arthroscopic Repair, Open Surgery in complex cases or severe instability and Rehabilitation.
Recurrent shoulder dislocation can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life and functional ability. Early diagnosis, appropriate evaluation, and proper treatment plans are key to managing this condition effectively. By understanding the causes, undergoing thorough evaluation, and exploring both conservative and surgical options, individuals with recurrent shoulder dislocation can work towards improved shoulder stability and reduced risk of future dislocations.
Dr. Anoop S. Pillai
Senior Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon
SUT Hospital, Pattom