- Emergency Ambulance Services
- 8606811111
- 0471-4077777, 0471-7177888
- gro@sutpattom.com
Presbycusis
Dr. Dhanashree A. Iyengar, Junior Consultant ENT, SUT Hospital, Pattom
Hearing loss associated with the physiological aging process in the ear is known as presbycusis. It usually manifest at around the age of 60years. But certain stressors can speed the rate of deterioration of hearing. The factors affecting the hearing loss are – age related, genetic, noise exposure, hormonal, ototoxic drugs etc.
With advancing age, there is anatomic and physiologic changes in the nerve and the nerve cells associated with hearing. Also, co-morbidities like Diabetes Mellitus, Hypertension, Renal (Kidney) disorders, dyslipidemia can also accelerate the hearing loss.
Individuals with chronic noise exposure and sustained noise induced inner ear damage in their youth tend to develop more severe noise induced hearing loss. Work related and environmental exposure to chemicals like – toluene, styrene, carbon monoxide, mercury, lead and also ototoxic medications – can accentuate the process of hearing loss. Recent studies have shown the role of hormonal factors too.
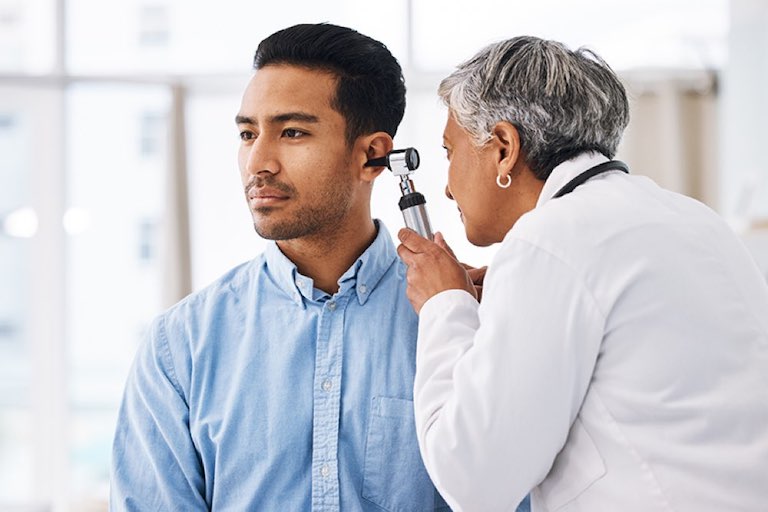
The typical presentation of presbycusis is gradual onset and slowly progressive hearing loss (in 1 or both ears). Mild cases are often difficult to detect. The family and friends are generally more aware of the hearing loss than the patient themselves. Tinnitus (ringing in the ear) may or may not be present. The patient usually complains of difficulty in discriminating speech with especially in a room with significant background noise.
Ear examination may show wax, discharge or fungal debris which should be cleared. The patients should then undergo a hearing test – PURE TONE AUDIOMETRY. The resulting audiogram graphically represents the hearing threshold of the patient at various loudness levels and frequencies (pitch).
Age related hearing loss cannot be use per se but if it can be treated with Hearing Aids, it may improve symptoms, delay complications and have a significant positive effect on the quality of life and communication. These are small electronic devices which may be worn behind or in the ear. They amplify the sounds so that the person can hear better in both noisy and quiet situations.
The hearing aids that will work best for the patient depend on the kind and severity of the hearing loss. It should be used regularly; hence it is important to choose one that is convenient and easy to use.
Factors to be considered while choosing:
- What features would be most useful to the patient?
- Total cost of the hearing aid.
- Do the benefits of newer technology outweigh the higher cost?
- Is there a trial period to test the hearing aid?
- Servicing and minor repairs.
Instructions and precautions
- Keep hearing aids away from heat and moisture.
- Clean hearing aids regularly as instructed.
- Avoid contact with hairsprays / perfumes.
- Turn off the hearing aid when not in use.
- Replace dead batteries immediately.
- Keep them away from children.