- Emergency Ambulance Services
- 8606811111
- 0471-4077777, 0471-7177888
- gro@sutpattom.com
Newborn Babies with Breathing Difficulty

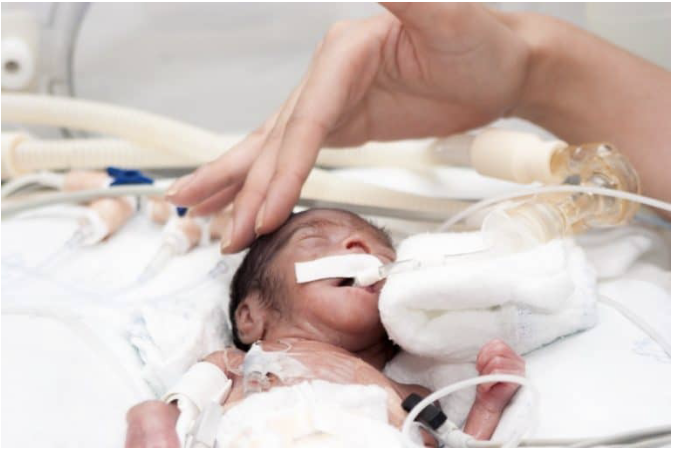
CPAP Support in a preterm baby with breathing difficulty
Dr Mrinal S Pillai, Consultant Neonatologist, SUT Hospital, Pattom
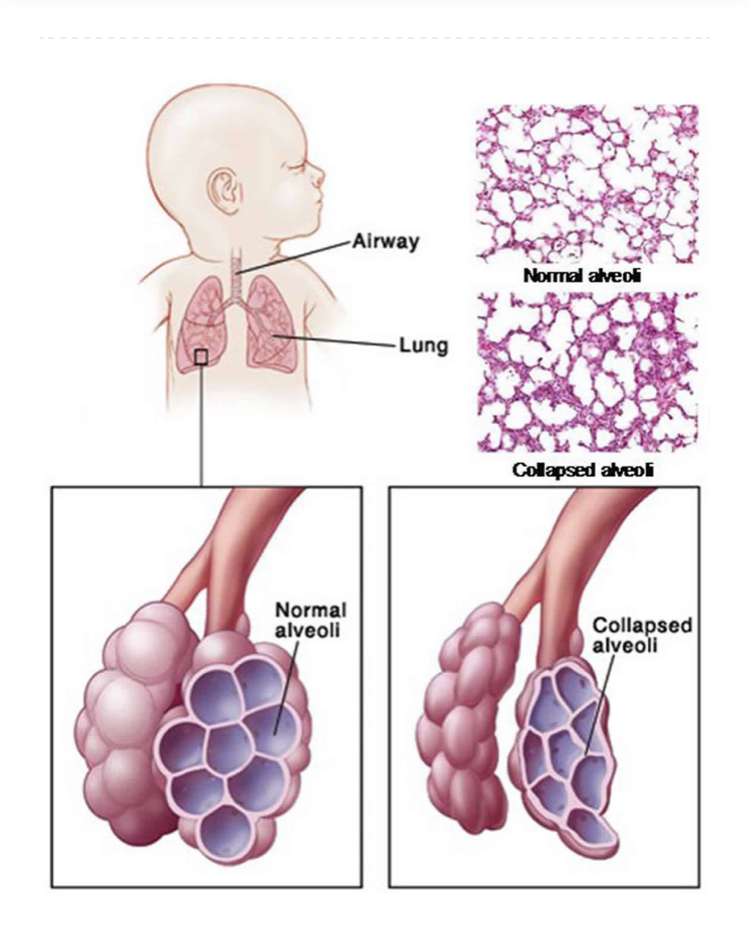
Breathing difficulty is also known as respiratory distress, which is the presence of fast breathing (respiratory rate > 60/ min in newborns) along with one of the following – nasal flare, chest retractions or grunting. Flaring of nose and chest retractions are movements of alae of nose and chest regions due to increased work of breathing. If the problem is severe, the baby may have central cyanosis (bluish discoloration of tongue /lips) due to low oxygen levels in blood. Respiratory distress in babies is a cause of significant morbidity and mortality. Severe respiratory distress may be present in 4 to 6% of live births.
There are various causes of respiratory distress such as Respiratory distress syndrome (RDS), Transient tachypnoea of newborn (TTNB), Pneumonia, Meconium aspiration syndrome (MAS), Asphyxial lung disease, Persistent pulmonary hypertension (PPHN), Congenital heart disease, pneumothorax, pleural effusion, aspiration of blood / feeds, metabolic causes such as hypoglycemia, acidosis. Rarely there are causes of respiratory distress which may need surgical intervention such as Tracheo-esophageal fistula, Diaphragmatic hernia, Lobar emphysema, Pierre -Robin syndrome, Choanal atresia.
Your baby’s doctor tries to find the cause of respiratory distress by checking the history of the baby for time of onset of distress, gestational age for prematurity, antenatal steroids (reduces risk of RDS in preterm babies), predisposing factors such as foul smelling liquor, prolonged rupture of membrane, peripartum fever, meconium stained amniotic fluid, and asphyxia. Examination of your baby by your doctor may also give him clues regarding the cause and severity of respiratory distress such as blood pressure, perfusion, cyanosis, chest examination, enlargement of liver, neurological status, features of sepsis, or any malformations. Features suggestive of severe respiratory distress suggest need for more advanced modes of support such as ventilation. Investigations such as White blood cell count, Neutrophil count, C-Reactive protein, Chest X-ray, Blood gas analysis may also help assessing the severity and differentiating various causes of respiratory distress.
Treatment of respiratory distress mainly consists of monitoring of vital signs such as Respiratory rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation; supportive care such as IV fluid, maintaining vital signs, oxygen therapy, respiratory support and specific interventions. Oxygen therapy is given in babies with respiratory distress who have central cyanosis or oxygen saturations less than 90 %. It is given after warming, humidification, blending with air to give specific concentration of oxygen depending on the baby’s need which may vary continuously. Continuous monitoring by well trained nursing staff and monitors is therefore of utmost importance. Hyperoxia, especially in preterm babies, is also avoided by judicious use of oxygen. Pulse oximetry is the equipment used for the non-invasive monitoring during oxygen therapy. The reading from Pulse oximeter is in the form of oxygen saturation (SpO2) which should be maintained between 90 – 95 % especially in preterm babies. Other parameters such as sensorium, temperature, perfusion and blood sugars are also monitored periodically as needed and maintained within normal range. Other respiratory supports include CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure), HFNC (High Flow Nasal Cannula), Ventilators, ECMO (Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenator), etc. Specific interventions include antimicrobials to treat pneumonia / infections, surfactant to treat respiratory distress syndrome, etc. Thus newborn babies with breathing difficulty need early recognition, timely referral, safe transport and appropriate treatment for their survival and better outcomes.

Severity of respiratory distress score

Oxygen Blender to provide oxygen therapy in babies
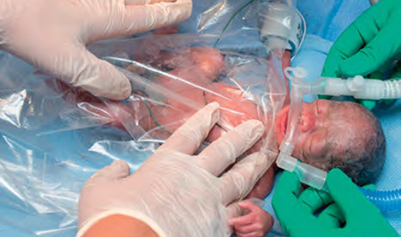
CPAP Support in a preterm baby with breathing difficulty
What is Respiratory-Distress-Syndrome in newborn
Infant respiratory distress syndrome causes, symptoms, diagnosis & treatment